GEO 302C EXAM 4 Fall 2003
The mean score of this test
is 86. Your grade was posted on eGradebook on 12/3/03.
You may not refer to any other materials during the exam. For each question (except otherwise explicitly stated), select the best answer for that question. Read all choices before selecting an answer and make sure your choice answers the question asked.
1. The past twenty years
or so, the size of the Antarctic ozone hole has increased to approximately as
large as the area of __________?
a. North America
b. Canada
c. USA
d.
e.
2. Near the Earth’s
surface ________ is a major component of urban smog, but it in the stratosphere
it protects life on Earth from harmful UV radiation.
a.
sulfur dioxide (SO2)
b.
carbon monoxide (CO)
c.
carbon dioxide (CO2)
d.
methane (CH4)
e. ozone (O3)
3. Which of the following
is not a greenhouse gas?
a. sulfur dioxide (SO2)
b. ozone (O3)
c. carbon dioxide (CO2)
d.
methane (CH4)
e.
water vapor (H2O)
4. Which of the following statements is not true of
carbon monoxide (CO)?
a.
it is the most plentiful of the primary pollutants
b.
it is a poisonous gas
c.
it is produced by the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
d.
roughly half of the CO in the atmosphere is produced by automobiles
e. it has increased considerably since the early 1970s
5. Volcanoes are an important natural source of:
a.
benzene
b. ozone
c. sulfur dioxide
d. carbon monoxide
e.
chlorofluorocarbons
6. A primary component of photochemical smog is:
a. ozone
b. carbon monoxide
c. sulfur dioxide
d. chlorofluorocarbons
7. The urban heat island
is:
a. warmer air temperatures in urban areas compared to surrounding
rural areas
b.
a concentration of energy use in an urban area
c.
locating factories in a single location downwind from cities
d.
use of conservation techniques to reduce energy use in cities
8. The problem of acid rain is probably most severe in which of
the following regions:
a.
b.
c. Desert Southwest
d.
e.
Central Plains
9. The so-called "ozone hole" is observed above:
a.
the continent of
b.
the equator
c.
the continent of
d. the continent of
e.
the continent of
10. Suppose it is warm and
raining, and a cold front is moving toward your location. Directly behind the cold front it is cold and
snowing. Still further behind the front
the weather is cold and clearing. If the
front is scheduled to pass your area in 6 hours, a persistence forecast for
your area for 12 hours from now would be:
a.
cold and snowing
b.
cold and clearing
c.
cold and cloudy
d. warm and raining
e.
not enough information on which to base a forecast
11. Which forecasting method assumes that weather systems will
move in the same direction and at the same speed as they have been moving?
a. persistence forecast
b. analogue forecast
c. climatological forecast
d. steady state (trend) forecast
12. Predicting the weather by weather types employs which
forecasting method?
a.
steady-state
b. analogue
c.
persistence
d.
guess
13. Suppose that where you live the middle of January is
typically several degrees warmer than the rest of the month. If you forecast this "January thaw"
for the middle of next January, you would have made a:
a.
forecast based on the analogue method
b.
persistence forecast
c.
forecast based on weather types
d. climatological forecast
14. Which of the following is not true in describing numerical weather predictions?
a.
computer forecast models may have flaws
b.
there are regions of the world where surface observations are sparse
c.
computer models of the atmosphere may contain chaotic behavior
d. the distance
between grid points on some models can always pick up smaller-scale weather
features such as thunderstorms
15. The forecasting of weather by a computer is known as:
a.
weather type forecasting
b.
climatology forecasting
c.
extended weather forecasting
d.
analogue prediction
e. numerical weather prediction
16. Modern computer forecasting models have increasingly smaller
grid spacing. This presents which of the following problems?
a.
mesoscale weather features can be predicted
b.
small-scale weather features can be resolved by the models
c. much more computations are needed
d.
none of the above
17. Ice cores record both the record of past temperatures, and
also the causes of climate change.
a. true
b.
false
18. The higher the ratio of oxygen 18 to oxygen 16 in the shells
of organisms that lived in the sea during the geologic past, the the climate at that time.
a. colder
b. warmer
c. wetter
d. drier
19. Which of the following is not true?
a.
oxygen 16 evaporates more readily from the ocean than oxygen 18
b. oxygen 16 and oxygen 18 are found in roughly equal amounts in
ocean water
c.
the nucleus of oxygen 18 contains two more neutrons than the nucleus of oxygen
16
d.
both oxygen 16 and oxygen 18 are found in the shells of marine organisms
20. A high concentration of oxygen 16 found in the ice caves of
a. cold air temperatures
b.
mild winters
c.
intense ultraviolet radiation
d.
the caves were under the ocean
21. Evidence suggests that throughout much of the earth's
history, the global climate was:
a. warmer than it is today
b.
colder than it is today
c.
about the same temperature as it is today
22. Which
of the following has been used to reconstruct past climates?
a.
analysis of air bubbles trapped in ice
b.
study of documents describing floods, droughts and crop yields
c.
the ratio of oxygen 18 to oxygen 16 in the shells of marine organisms
d.
study of geologic formations
e. all of the above
23. During the Pleistocene epoch:
a.
continental glaciers continuously covered large parts of
b.
it was much warmer than now
c.
continental glaciers alternately advanced and retreated over large portions of
d.
tropical vegetation was growing over vast regions of the Central Plains of
e.
sea level was higher than today
24. Thick sheets of ice advanced over
a. 1816 ("the
year without a summer")
b. 1550
c. 18,000 to 22,000 years ago
d.
2 million years ago, at the beginning of the Pleistocene epoch
e.
during the Cretaceous age
25. Over the past 100 years or so, it appears that average yearly
global temperatures have:
a. increased slightly
b.
fluctuated widely but shown no overall change
c.
decreased slightly
d.
remained constant
26. The Viking colony in
a.
the Pleistocene epoch
b.
the climatic optimum
c. the Little Ice Age
d.
the explosion of
e.
the Industrial Revolution
27. The Medieval Climatic Optimum was a relatively _________
period.
a.
cold
b. warm
28. During the Little Ice Age:
a.
the climatic optimum occurred
b.
the Bering land bridge formed
c. alpine glaciers grew in size and advanced
d.
continental glaciers covered large portions of
e.
sea level lowered by about 280 ft
29. If the earth were in a cooling trend, which process below
would most likely act as a positive feedback mechanism?
a. increasing the snow cover around the earth
b.
increasing the water vapor content of the air
c.
decreasing the amount of cloud cover around the globe
d.
increasing the carbon dioxide content of the air
30. If the earth were in a warming trend, which of the processes
below would most likely act as a negative feedback mechanism?
a.
increasing the water vapor content of the air
b. increasing the snow cover around the earth
c.
decreasing the amount of cloud cover around the globe
d.
increasing the carbon dioxide content of the air
31. The Milankovitch Theory proposes that climatic changes are
due to:
a. variations in the earth's orbit as it travels through space
b.
volcanic eruptions
c.
changing levels of CO2 in the earth's atmosphere
d.
particles suspended in the earth's atmosphere
32. During a period when the earth's
orbital tilt is at a minimum, which would probably not be true?
a.
there should be less seasonal variation between summer and winter
b.
more snow would probably fall during the winter in polar regions
c. there would be a lesser likelihood of glaciers at high latitudes
d.
there would be less seasonal variations at middle latitudes
33. Precession of the equinox refers to:
a.
changes in the shape of the earth's orbit as the earth revolves around the sun
b.
changes in the tilt of the earth as it orbits the sun
c.
changes in the seasons, especially from winter to summer
d. the wobble of the earth on its axis
34. The Milankovitch cycles in association with other natural
factors explain how glaciers may advance and retreat over periods of:
a.
hundreds of millions of years
b.
several million years
c.
hundreds of thousands of years
d. ten thousand years to one hundred thousand years
e.
hundreds of years
35. The formation of continental glaciers over vast areas of
a.
cool, extremely cold
b. cool, mild
c.
warm, extremely cold
d.
warm, mild
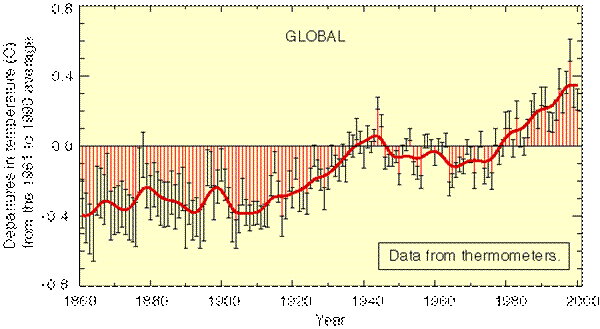
The above figure shows annual changes (anomalies) of
the average global surface air temperature from 1861 to 2000 relative to 1961 to
1990 which is considered to be the baseline period. Please use this figure when
answering Questions 36-40.
36.
Which of the following statements is correct in describing the climate over the
past 140 years:
a. mostly
cold but with an overall warming trend
b. mostly warm but
with an overall cooling trend
c. mostly warm but
without any trend
d. mostly cold but
without any trend
e. none of the
above
37. Which of the following statements is correct in
describing the climate over the past 25 years:
a. mostly cold but
with a strong warming trend
b. mostly
warm with a strong warming trend
c. mostly warm but
without any trend
d. mostly cold but without any trend
e. none of the above
38. Which decades represent
the warmest decades over the past 140 years?
a. 1960s
b. 1970s
c. 1980s
d. 1990s
39. Which year represents the
warmest year over the past 140 years?
a. 1996
b. 1997
c.
1998
d. 1999
e. 2000
40. Which of the following is correct in describing
the overall temperature trend over the past century?
a. a warming by about 1.7°C
b. a warming by about 0.7°C
c. a cooling by about 0.7°C
d. a cooling by about 1.7°C
41. The climate of the last 1000 years can be
characterized as:
a. a Medieval Warm Period, a cold Little
Ice Age, and a warming trend since the late 19th century
b. a Younger-Dryas cold spell, a cold Little Ice Age, and a
warming trend since the late 19th century
c. a mid-Holocene maximum, a Medieval Warm Period, and a
cold Little Ice Age
d. a predominantly warm period
e. all of the above.
42.
The climate of the last 1 million years can be characterized as:
a. mostly
cold with relatively short warm periods
b. mostly cold but
with a strong warming trend
c. mostly warm but
with very strong glacial periods
d. mostly warm and
dry
e. all of the
above.
43. Which of the following is in the correct
sequence from long to short term effects on climate?
A.
eccentricity – mountain building – El Nino – seasonal changes in monsoon
intensity
B. plate
tectonics – Earth’s orbital parameters – ENSO – seasonal changes in latitudinal
distribution of insolation
C. mountain
building – the Southern Oscillation – precession - seasonal changes in
latitudinal distribution of insolation
D.
eccentricity – obliquity – precession – the ocean conveyor belt – ENSO
E. both B and D are correct
44. Which of the following is NOT true about the Milankovitch Cycles?
a. They explain glacial and interglacial
intervals during the current Icehouse climate period.
b. One part of the cycle is the change in
the tilt of the Earth about every 40,000 years.
c. One part of the cycle is the change in
the shape of the Earth’s orbit over time scales of 100,000 years.
d. The cycles have been supported by the trends of atmospheric CO2,
CH4, and temperature as recorded in the Antarctic ice core.
e. One part of the cycle is the wobbling
of the spin axis about every 10,000 years.
45. Two
examples of human activities that can explain the steady increase in the
atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration since the Industrial Revolution are:
A. burning fossil fuels and cutting trees
B. building
dams and growing trees
C. using
wind energy and collecting solar energy
D. none of
the above
46. Large volcanic eruptions with an ash veil that enters the stratosphere, tend to ___ at the surface.
a.
increase temperatures
b.
increase precipitation
c. decrease temperatures
d.
have no effect
47. Studies reveal that during colder glacial periods, CO2
levels during warmer interglacial periods.
a.
were higher than
b. were lower than
c.
were about the same as
d.
were more variable than
48. The most recent warming trend
experienced over the Northern Hemisphere could be the result of:
a.
increasing volcanic eruptions
b.
light colored particles in the stratosphere
c. increasing levels of CO2
d.
a decrease in the energy emitted by the sun
e.
an observed decrease in snow cover
49. Everything else being equal, a gradual increase in global CO2
would most likely bring about:
a. an increase in surface air temperature
b.
a marked decrease in plant growth
c.
a decrease in evaporation from the earth's oceans
d.
no change in global climate
50. The much-studied temperature record of the past 140 years is
derived from
a.
land-based thermometer readings only
c.
satellite-based observations only
b.
ocean-based thermometer readings only
d.
tree ring records
e. both land- and ocean-based thermometer readings