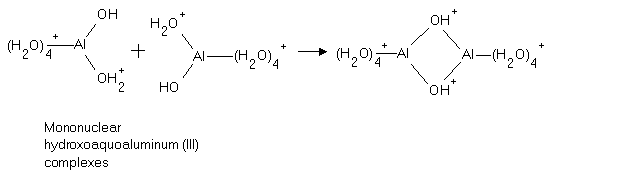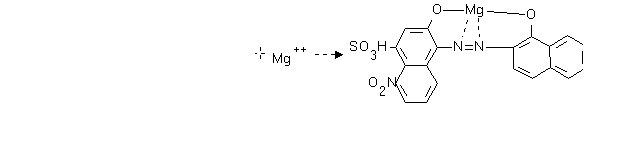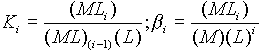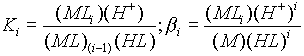- Coordination compounds are complexes that consist of one or more central atoms
or ions with one or more attached molecules
- The central atom is called a metal, and is a Lewis Acid;
- The attached ions are ligands, and are Lewis Bases;
- The total number of attachments between metal and ligands is the coordination number
- Ligands attach to the metal via coordinate covalent bonds, i.e., the electrons of
the bond is entirely derived from the ligand.
- Must involve electron pair not otherwise utilized in bonding withing the ligand.
The electron pair is equally shared, but controlled by the ligand.
- The ligand is a lewis base, and acts as an electron pair donor. The metal
is the electron acceptor and a lewis acid.
- Most metals form cationic ions in solutions (electron acceptors), and participate in
coordination complexes.
- The strength of the coordination interaction is a function of the ability of a ligand to
donate or share their available pair(s) of electrons.
- Coordination number of a metal ion may vary from one complex to another.
Fe(H2O)6+3 ; Fe(CN)6-3
;' Fe(Cl)4-
- Water is also a (weak) Lewis Base, and can act as a ligand.
Aqueous ions are almost always initially coordinated with water, and any other
complex actually forms by ligand exchange between water and the new
ligand, i.e.:
Fe(H2O)62+ + Cl-
<----> Fe(H2O)5Cl+ + H2O
- . Ligands that attach at a single point are monodentate.
Examples are Cl-, CN-, OH-
- Multidentate ligands chelate the metal, Ex. SO42-
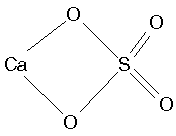
EDTA, for example,. forms 6-dentate complexes:
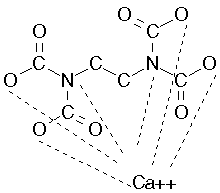
11. Polynuclear complexes form when there is more than one central ion or
molecule:
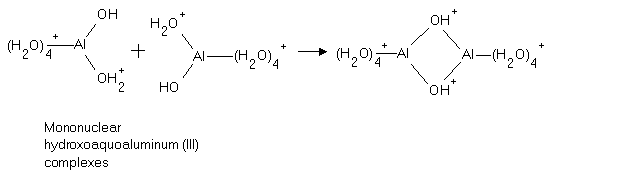
Ion Pairs
- Temporary electrostatic complexes where each ion
retains their coordinated waters, but they are still close enough to effectively form a
complex between the metal and the ligand.
- Usually form beween Hard cations and anions
- Another term is outer sphere complex. These complexes
are difficult to analyze directly, and are normally estimated from coulombic attraction
and Bejerrum's ion association model;
- The log Kstab of ion pair complexes range from ~0 to 4, depending on
charge density
- There can be ion pair or coordinative complexes for the same
pair of ions, with an equilibrium established between them. The major ion pairs in
water are:
CaHCO3+, ; CaSO4°; CaOH+;
MgCO3°; MgSO4°
- The degree of interaction is only slightly greater than the electrostatic interactions
accounted for by the DeBye-Huckel theory, but this is enough to change activities.
- Ion pairs become more important in saline waters and brines, where the interactions must
be specifically accounted for using the Pitzer Equations.
Reaction Rate:
- The rates of coordination reactions are characterized by the terms labile (very
fast reactions) and inert (very slow reactions).
- These terms do not necessarily indicate the stability of the complex, only the
kinetics.
- Ligand exchange involving water is usually fast, on the order of seconds
- Equilibrium constants for complexes are usually stated for reactions written in the
direction of complex formation, that is a stability constant:
Ligand + central metal ion -----> Complex
- The Keq of the reaction is the stability or formation constant.
Large values of stability constants indicate stable complexes. If
the equilibrium constant is stated for the dissociation of the complex, it is called a dissociation
or and instability constant.
HSAB
- Complex stability can be predicted in a general sense by the HSAB appraoch, or Hard
soft acid bases rules. The basic premise is that an individual cation
"prefers" to to bond with one type of ligand over another
- Type A metals tend to be sperically symetrical, with intert gas electron
configurations, and are known as hard spheres, or hard acids. Examples are:
Alkalis; Na+, K+ (Weakest interaction, rarely considered)
Alkaline earths; Ca+2, Mg2+;
Al+3; Th+4; Si+4
These cations tend to complex F- and ligands containing oxygen;
CO32-; OH-; Borate
- B-type cations have more easily polarized electron
shells, form covalent complexes, and are termed soft acids, e.g.:
Ag+; Zn+2; Hg+2; Pb+2, Sn+2.
These metals tend to form complexes with soft ligands containing I, S, P, and N.
NH4+; S-; PO3-3 (Phosphite)
- ClO4- and NO3- rarely complex metals, while
phosphate, hydroxide, and carbonate are potent complex formers.
- Complexes containing 5 and 6 membered rings are the most stable, while four or 7+
membered rings are less stable.
- Stability increases with the number of attachment points, so multiligand complexes are
more stable than monodentate, called the chelate effect.
- When a ligand forms complexes with two metal ions at equal concentration in a solution,
the ligand will form complexes preferentially with the metal ion that produces the complex
with the larger stability constant. Example: EDTA titration of hardness
Ca2+ + EDTA4- <----> (EDTA-Ca)2-:
K = 10+10.7
Mg2+ + EDTA-2 <----> (EDTA-Mg)-2:
K = 10+8.7
Since the stability constant of the calcium complex is significantly larger than the Mg
complex, the reaction with calcium proceeds to completion before any reaction with
magnesium:
!!remember, as metal is complexed its concentration decreases, changing the releation
to the equilibrium constant.
- When a ligand that forms a very stable complex with a metal ion is added to a solution
of the metal ion complexed with another ligand in a less stable complex, the stronger
complexing agent (ligand) will tend to decompose the existing complex and withdraw the
metal ion into a complex with itself (assuming the weaker complex is labile):
Example, EDTA Hardness titration:
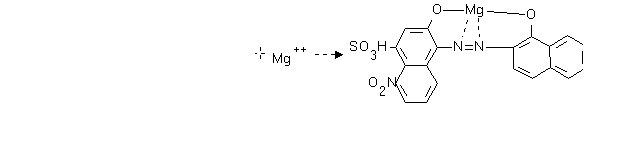
A solution containing both Mg and Ca is dosed with the complexing agent Erichrome
Black T (EBT), which forms a complex with Mg2+. The EBT-Mg complex
(K = 10+7) is weaker than the EDTA-Mg complex (K=10+8.7)
The color of the EBT-Mg complex is red, and the color of uncomplexedd EBT is blue. A
solution with excess EBT is therefore purple. Adding EDTA, the color of the solution will
change from Purple to pure blue as the Red EBT-Mg complex is consumed.